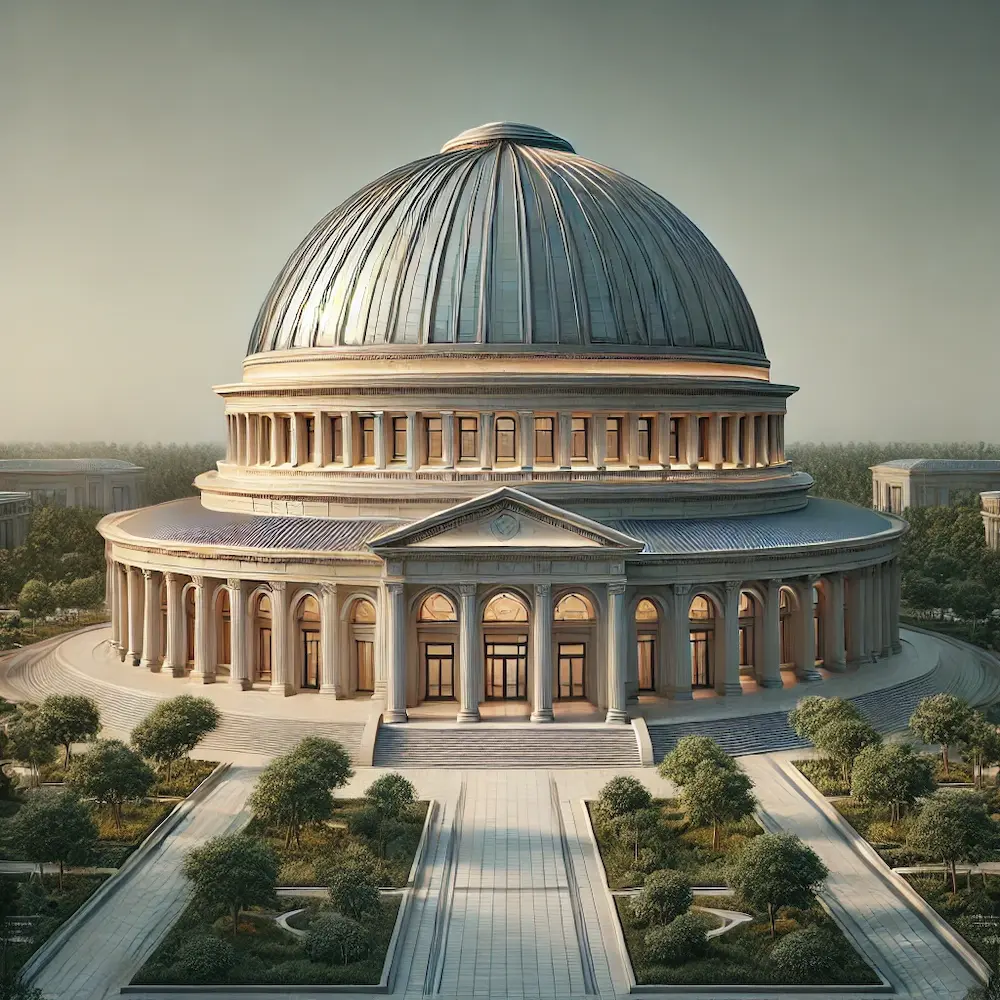
A dome roof is a hemispherical structure that serves as the ceiling or roof of a building. Its curved shape offers both aesthetic appeal and structural advantages, making it a prominent feature in various architectural styles throughout history.
History and Origins of Dome Roofs
The use of domes dates back to ancient civilizations. Early examples include round huts and tombs in the Middle East, India, and the Mediterranean. The Romans advanced dome construction by introducing large-scale masonry hemispheres, exemplified by structures like the Pantheon in Rome, built around 126 AD. This architectural form was further refined during the Byzantine era, with notable examples such as the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul, constructed in the 6th century. Over time, domes became integral to Islamic architecture, Renaissance cathedrals, and modern structures worldwide.
Key Features of Dome Roofs
Dome roofs are characterized by their curved, hemispherical shape, which allows for a spacious interior without the need for supporting columns. This design efficiently distributes weight and provides resistance against external pressures like wind and earthquakes. Variations of dome designs include:
- Hemispherical Domes: Classic half-sphere shapes, as seen in the Pantheon.
- Onion Domes: Bulbous, pointed domes typical in Russian and Indian architecture.
- Geodesic Domes: Composed of a network of triangles, offering a lightweight yet strong structure.
Applications of Dome Roofs
Throughout history, dome roofs have been utilized in various structures, including:
- Religious Buildings: Churches, mosques, and temples often feature domes symbolizing the heavens.
- Government and Civic Buildings: Capitols and courthouses use domes to convey grandeur and authority.
- Cultural Institutions: Museums and theaters incorporate domes for their acoustic properties and visual impact.
- Modern Architecture: Contemporary designs employ geodesic domes for sports arenas, exhibition halls, and eco-friendly homes.
Considerations When Choosing Dome Roofs
When opting for a dome roof, several factors should be considered:
- Structural Integrity: Ensuring the foundation and materials can support the dome’s weight.
- Materials: Selecting appropriate materials, such as concrete, steel, or modern composites, based on the design and purpose.
- Climate: Considering insulation and ventilation needs, especially in extreme weather conditions.
- Aesthetics: Aligning the dome’s design with the overall architectural style of the building.
- Cost: Evaluating the budget, as dome construction can be more expensive than traditional roofing methods.
Conclusion
Dome roofs have played a significant role in architectural history, offering both functional benefits and symbolic meaning. From ancient temples to modern eco-friendly structures, their versatility and beauty continue to inspire architects and builders worldwide.